- An astronomer says that he has discovered nickel in an object in space.
How does he know that nickel is there?
- Sketch an emission line spectrum, and label appropriately.
- You see a continuum spectrum. What does this tell you about the source?
- The spectrum of a star is found to peak at 0.87 mm. What is its temperature?
- Suppose the temperature of a star is 6000 K. Suppose the star's radius suddenly
increased by a factor of 4 but its luminosity does not change. What temperature
would the star have to change to so that its luminosity remained constant with the
change in radius?
- List the ways in which energy can be transported from one location to another, and
give an example of each
- What is the most stable element to fission and fusion? What do we mean by this?
- Atom A and atom B are identical atoms. Suppose an electron in atom A falls from quantum
level 4 to quantum level 1, emitting a photon. In atom B an electron falls from level 4
to level 2. Which photon has the shortest wavelength?
- Suppose a star is orbiting a black hole. Explain how you could tell the star is in orbit
around the black hole by observing its spectrum at different times (places in its orbit).
Hint: Drawing a picture of the system at different times might help.
- Give two reasons why bigger telescopes are better.
- Suppose an experiment can measure parallaxes of stars to 0.01 arcseconds. Can this
experiment measure the distance to a star that is 1000 pc away?
- When the sun ends its life (after the red giant stage) it will become a white dwarf.
What would be the spin-rate of this white-dwarf?
- Two stars are observed to have an orbital period of 6 years. If their separation is 6 AU,
what is the mass of the system?
- A telescope operating at a wavelength of 0.5 mm has a spatial resolution of 3 arcseconds.
Suppose the telescope now operates at 1.5 mm. What is the spatial resolution of the telescope
operating at this new wavelength? (Ignore any atmospheric effects.)
- A spectral line in a star is observed to be at 4800 A. It is known that this line is normally
located at 5000 A. Is the star moving towards or away from us? What is its velocity?
- Suppose the sun was instantaneously replaced by a black hole of the same mass. Which of the
following statements are true?
- Mercury, Venus and the Earth would be swallowed up.
- The Earth's oceans would freeze.
- Nothing would happen to the orbit of the Earth.
- The Earth's oceans would boil.12. Circle the following that were true in the early universe
compared to today.
- In the early universe -
- Temperatures were lower.
- Galaxies were closer together.
- Radiation dominated over matter.
- The sun did not exist.
- Suppose Hubble's constant (
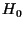 ) is 100
) is 100
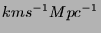 A galaxy is observed to be moving
with a velocity of 10,000 km/sec. How far away would you estimate the galaxy to be?
A galaxy is observed to be moving
with a velocity of 10,000 km/sec. How far away would you estimate the galaxy to be?
- Suppose under the assumption that the lifetime of a technical civilization is
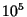 years, we estimate
that there are
years, we estimate
that there are 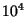 civilizations in the galaxy. How many would you expect if the lifetime of a
technical civilization were
civilizations in the galaxy. How many would you expect if the lifetime of a
technical civilization were 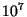 years?
years?
- A planet is found around a star that is 81 times more luminous than the sun. This planet is located 16 AU
from the star. Will this planet be warmer or cooler than the earth?
- Our Sun is not a first generation star. How do we arrive at this conclusion?
Sushan Konar
2004-02-20